Classification of Chinese calligraphy

[http://blog.yam.com/artie69/article/20657642]
Chinese poem, calligraphy, traditional painting, poetry, drama and opera make up of mysterious Chinese culture. Writing and utilization of Chinese characters can trace back to inscription on oracle bones or bird-and-insect script. Generally, seal character, clerical script, regular script, cursive script and running script are the most important pillars in evolution process.
1) Inscription on oracle bones
Inscription on oracle bones is the cultural product of Shang Dynasty (BC17-BC11). Due to superstitious belief in ghosts and spirits, people always practiced divination by use of tortoise shell and animal bones before works and recorded the divined matters and the fulfilled oracle inscriptions on tortoise shell and animal bones.

2) Inscriptions on ancient bronze objects
It emerges latter than inscription on oracle bones, which means the typecasting or inscriptions on ancient bronze objects. It is neat, robust, pretty, simple, unsophisticated and good-mannered, taking Duke Mao Tripod as representative.
3) Large seal script
Large seal script is a character utilized commonly in Western Zhou Dynasty, which was created by Yi according to legend. In view of different writing mediums, large seal script is also classified as inscriptions on ancient bronze and script of Zhou Dynasty.
4) Script of Zhou Dynasty
Script of Zhou Dynasty is the character used by ancient Qin Dynasty and the predecessor of small seal character, where, Zhou means “read aloud”, with Inscriptions on Drum-shaped Stone Blocks as the representative.
5) Small seal script
It is said that after unification of the country by Emperor Qin Shihuang, Li Si implemented the policy of unified transport system, single written language, simplified on the basis of large seal script and script of Zhou Dynasty, fixed the component, direction and pattern of characters and unified the written form of Chinese characters. Small seal script is beautiful and has been always favored by calligraphist and seal cutter.
6) Carved symbols
Seal character carved on tally in Qin Dynasty, e.g. words in Yangling Tiger-shaped Tally.
It emerges latter than inscription on oracle bones, which means the typecasting or inscriptions on ancient bronze objects. It is neat, robust, pretty, simple, unsophisticated and good-mannered, taking Duke Mao Tripod as representative.
3) Large seal script
Large seal script is a character utilized commonly in Western Zhou Dynasty, which was created by Yi according to legend. In view of different writing mediums, large seal script is also classified as inscriptions on ancient bronze and script of Zhou Dynasty.
4) Script of Zhou Dynasty
Script of Zhou Dynasty is the character used by ancient Qin Dynasty and the predecessor of small seal character, where, Zhou means “read aloud”, with Inscriptions on Drum-shaped Stone Blocks as the representative.
5) Small seal script
It is said that after unification of the country by Emperor Qin Shihuang, Li Si implemented the policy of unified transport system, single written language, simplified on the basis of large seal script and script of Zhou Dynasty, fixed the component, direction and pattern of characters and unified the written form of Chinese characters. Small seal script is beautiful and has been always favored by calligraphist and seal cutter.
6) Carved symbols
Seal character carved on tally in Qin Dynasty, e.g. words in Yangling Tiger-shaped Tally.
7) Bird-worm seal script:
It is also called as “worm seal script” and is the decorated letter in seal script. It forms stokes by use of animal rudiment, like calligraphy and painting, very interesting.
8) Appointment script
All appointment letters are called as appointment script, also called as Bangshu Script.
9) Stone-drum inscriptions
It is a transition script from inscriptions on ancient bronze objects to small seal script, also called as hunting script or Yongyi inscription, which is the earliest extant inscription in China. It is straight forward, strict and neat, with uniform stroke thickness. Stone drum is China’s first ancient object and the first rule for calligraphers, with high literary and historic values and art collection value.
10) Jade-chopstick seal
It is a kind of seal characters, which is round and gentle, just like jade chopstick, thus is called as jade-chopstick seal.
11) Iron-wire seal
It is a kind of small seal, which is round, flexible, like an iron wire, thus is called as iron-wire seal.
12) Clerical script:
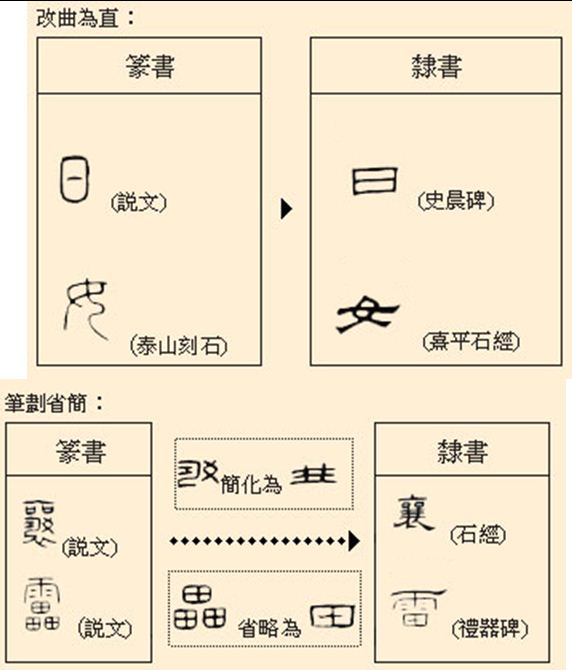
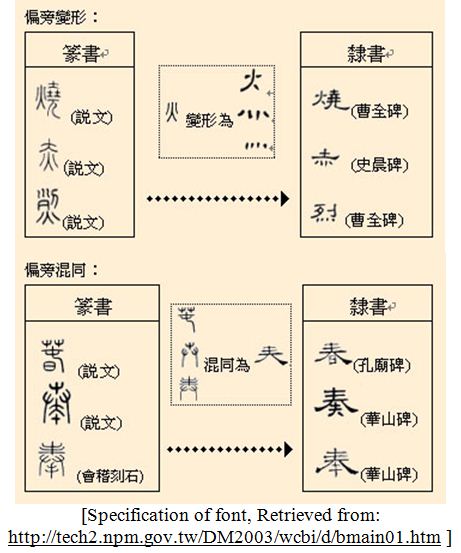
It is flat and square, thus is easy to write. It originates from Qin Dynasty, was widely used in Han and Wei Dynasties, which transforms from seal in four parts: change the roundness to straightness, simplify the strokes, deform the character component and combine the components. It broke through the character structures, laid a foundation of regular script, thus was the turning point in Chinese character evolution history and calligraphy history.
It is also called as “worm seal script” and is the decorated letter in seal script. It forms stokes by use of animal rudiment, like calligraphy and painting, very interesting.
8) Appointment script
All appointment letters are called as appointment script, also called as Bangshu Script.
9) Stone-drum inscriptions
It is a transition script from inscriptions on ancient bronze objects to small seal script, also called as hunting script or Yongyi inscription, which is the earliest extant inscription in China. It is straight forward, strict and neat, with uniform stroke thickness. Stone drum is China’s first ancient object and the first rule for calligraphers, with high literary and historic values and art collection value.
10) Jade-chopstick seal
It is a kind of seal characters, which is round and gentle, just like jade chopstick, thus is called as jade-chopstick seal.
11) Iron-wire seal
It is a kind of small seal, which is round, flexible, like an iron wire, thus is called as iron-wire seal.
12) Clerical script:
It is flat and square, thus is easy to write. It originates from Qin Dynasty, was widely used in Han and Wei Dynasties, which transforms from seal in four parts: change the roundness to straightness, simplify the strokes, deform the character component and combine the components. It broke through the character structures, laid a foundation of regular script, thus was the turning point in Chinese character evolution history and calligraphy history.
13) Grass seal:
It is the seal written in cursive form, also called as calligraphy with hollow strokes.
14) Tadpole script:
It is the vulgo of hand-written seal. Since there was no pen and ink in ancient times, thus bamboo strip was used to dip into the lacquer and write on the bamboo. Since the bamboo is hard and lacquer is greasy, thus it is thick at the head but thin at the tail, just like a tadpole, thus it is called as tadpole script.
15) False seal script
It is a kind of seal for stamp patterning, which is square and uniform, just like regular seal; its handwriting changes from round and tactful to buckling and winding, with an affectionateness meaning, hence gaining its name.
16) Regular script
It generates in Qin and Han Dynasties, with a writing patterned in Three Kingdoms. Regular script developed vigorously in Wei, Jin, Northern and Southern Dynasties, with Wang Xizhi’s script as its representative. It is also called as standard script, clerical script, modern clerical script, Bafen-style script, etc. It is square and flush, unlike the longitudinal small seal script or flat seal script. It has ticks but not upstrokes and uses broken but not turning transitions, in a right to left writing pattern.
17) Empire script
It is one kind of regular script, which is rigid, sharp and thin, in a plump and free style. PMingLiu script just derivates herefrom.
18) Cursive script
It means illegible writing in whatever eras in broader understanding, but the continuous and convenient script in narrow sense. Cursive regular script was current at earlier period of Han Dynasty, then developed into memorial cursive gradually and became the modern cursive with continuous and convenient strokes, i.e. the cursive called by later generations.
19) Wild cursive:
It is also called as Large Cursive and the most unrestrained cursive script. It is uninterrupted and rush, most changeful, lively and vigorous, with Four Poems of Old by Zhang Xu and Autobiography by Huai Su as the representatives.
20) Running calligraphy
It is also called as Running Script. It is said that it was created by Liu Desheng at end of Han Dynasty. Running script is written fluently and conveniently on the basis of regular script. It is not that unrestrained or difficult to distinguish like cursive script and vivider and simpler than regular script, thus is a hand-written calligraphy widely used in society. Writing brush or pen is not stopped, written on paper in an appropriate dynamics and in a freely flowing style.
It is the seal written in cursive form, also called as calligraphy with hollow strokes.
14) Tadpole script:
It is the vulgo of hand-written seal. Since there was no pen and ink in ancient times, thus bamboo strip was used to dip into the lacquer and write on the bamboo. Since the bamboo is hard and lacquer is greasy, thus it is thick at the head but thin at the tail, just like a tadpole, thus it is called as tadpole script.
15) False seal script
It is a kind of seal for stamp patterning, which is square and uniform, just like regular seal; its handwriting changes from round and tactful to buckling and winding, with an affectionateness meaning, hence gaining its name.
16) Regular script
It generates in Qin and Han Dynasties, with a writing patterned in Three Kingdoms. Regular script developed vigorously in Wei, Jin, Northern and Southern Dynasties, with Wang Xizhi’s script as its representative. It is also called as standard script, clerical script, modern clerical script, Bafen-style script, etc. It is square and flush, unlike the longitudinal small seal script or flat seal script. It has ticks but not upstrokes and uses broken but not turning transitions, in a right to left writing pattern.
17) Empire script
It is one kind of regular script, which is rigid, sharp and thin, in a plump and free style. PMingLiu script just derivates herefrom.
18) Cursive script
It means illegible writing in whatever eras in broader understanding, but the continuous and convenient script in narrow sense. Cursive regular script was current at earlier period of Han Dynasty, then developed into memorial cursive gradually and became the modern cursive with continuous and convenient strokes, i.e. the cursive called by later generations.
19) Wild cursive:
It is also called as Large Cursive and the most unrestrained cursive script. It is uninterrupted and rush, most changeful, lively and vigorous, with Four Poems of Old by Zhang Xu and Autobiography by Huai Su as the representatives.
20) Running calligraphy
It is also called as Running Script. It is said that it was created by Liu Desheng at end of Han Dynasty. Running script is written fluently and conveniently on the basis of regular script. It is not that unrestrained or difficult to distinguish like cursive script and vivider and simpler than regular script, thus is a hand-written calligraphy widely used in society. Writing brush or pen is not stopped, written on paper in an appropriate dynamics and in a freely flowing style.